Java access modifiers are used to provide access control in java. Java provides access control through three keywords – private, protected and public. We are not required to use these access modifiers always, so we have another one namely “default access“, “package-private” or “no modifier“.
We can use java access modifiers with Classes as well as Class variables and methods.
We are allowed to use only “public” or “default” access modifiers with java classes.
- If a class is “public” then we can access it from anywhere, i.e from any other class located in any other packages etc.
- We can have only one “public” class in a source file and file name should be same as the public class name.
- If the class has “default access” then it can be accessed only from other classes in the same package.
Java Access Modifiers with Class Member
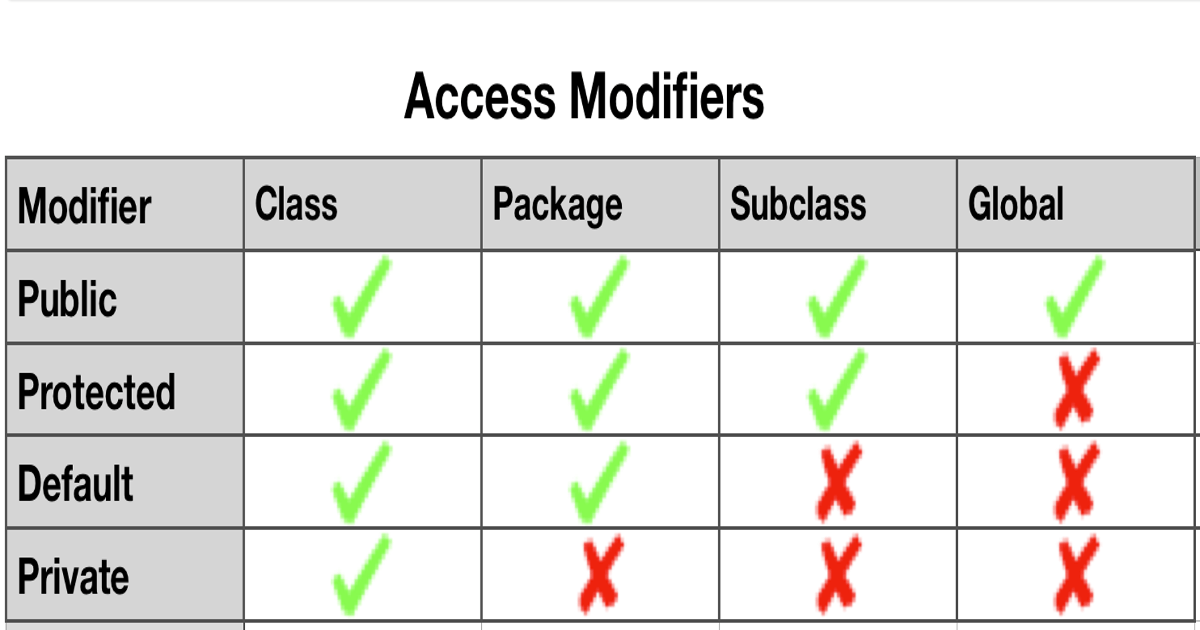
We can have all the four access modifiers for class member variables and methods. However member access modifier rules get applied after the class level access rules. For example, if class is having default access then it will not be visible in other packages and hence methods and variables of the class will also be not visible.We will look into each of them separately and then we will show the java access modifiers usage with simple program.
Java Access Modifiers – public keyword
If class member is “public” then it can be accessed from anywhere. The member variable or method is accessed globally. This is simplest way to provide access to class members, however we should take care in using this keyword with class variables otherwise anybody can change the values. Usually class variables are kept as private and getter-setter methods are provided to work with them.Java Access Modifiers – private keyword
If class member is “private” then it will be accessible only inside the same class. This is the most restricted access and the class member will not be visible to the outer world. Usually we keep class variables as private and methods that are intended to be used only inside the class as private.Java Access Modifiers – protected keyword
If class member is “protected” then it will be accessible only to the classes in the same package and to the subclasses. This modifier is less restricted from private but more restricted from public access. Usually we use this keyword to make sure the class variables are accessible only to the subclasses.Java Access Modifiers – default access
If class member doesn’t have any access modifier specified, then it’s treated with default access. The access rules are similar as classes and the class member with default access will be accessible to the classes in the same package only. This access is more restricted than public and protected but less restricted than private.Below table summarise above access modifiers with respect to different classes in the same package or other package and subclasses.